Types of Poems – Ways of Blending Meaning, Sound, and Rhythm
This post may contain affiliate links. We may earn a small commission from purchases made through them, at no additional cost to you.
There are many types of poems out in the big wide world, and they are all deserving of some level of attention. This article will examine fifteen different poem styles to give a quick glimpse into the larger overall world of poetry. There are many different types of poems, structures, themes, techniques, and other poetic elements to know. Let’s have a look at a few of them and identify some of the most common types of poems.
Table of Contents
The Types of Poetry
We are going to look at fifteen different types of poems with examples below. It is worth noting that this is not an exhaustive list of poem styles and structures, but it should be a good general overview. In addition, this list is in alphabetical order and that is why the most famous types are not lifted to the top of the list. So, let’s get started and have a look at the different types of poems, structures, and varieties.
Acrostic Poetry
| Place of Origin | Ancient Greece |
| Era of Origin | Around 330 – 220 BCE |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | Acrostic by Lewis Carrol |
Acrostic poems are a rather entertaining type of poetry that is, typically, not considered to be all that elite in comparison to some of the other types of poems that exist in the world. In very basic terms, an acrostic poem is a type of poem that includes a vertical component, such as spelling out a name or word with the first letter of every line.
 December an acrostic from Little Snow White and other stories published by A. L. Burt Company (1906); A. L. Burt Company (publisher), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
December an acrostic from Little Snow White and other stories published by A. L. Burt Company (1906); A. L. Burt Company (publisher), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
An acrostic poem does not need to make use of the first word of every line, and the spelled-out element could be found in other vertical parts of the poem, but the first word is the easiest way to do this.
This is probably one of the better-known poem styles even when someone does not know the name of this type of poem. There are not all that many examples of this particular type of poetry that are necessarily all that famous, but perhaps the most famous is a poem called Acrostic by Lewis Carroll (of Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland fame).
Ballad Poetry
| Place of Origin | France |
| Era of Origin | 15th century |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | ABAB and/or ABCB |
| Famous Example | The Rime of the Ancient Mariner by Samuel Taylor Coleridge |
The ballad is one of the most famous types of poetry. This particular form is an example of narrative poetry and, in a traditional sense, this particular type of poetry was also set to music. However, this is not necessary. The traditional ballad would often tell the stories of heroes and folkloric figures in some descriptive detail, but the ballad structure has actually been adopted in contemporary times because of its musical and deeply emotive qualities.
 The Last Ballad by Henri Toulouse-Lautrec (1893); National Gallery of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Last Ballad by Henri Toulouse-Lautrec (1893); National Gallery of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
This particular type of poem generally makes use of a quatrain structure with an ABAB or ABCB rhyme scheme structure (although contemporary versions may be looser with these elements, and because of this basic structure, the ballad can be found in much of contemporary music.
An additional reason for the use of the ballad as a standard musical form is because they usually include the use of refrains, and this has been translated into the modern-day chorus.
Blank Verse Poetry
| Place of Origin | Italy |
| Era of Origin | 16th century |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | Paradise Lost by John Milton |
Blank verse poetry is somewhat similar to free verse poetry, but there are some important distinctions. This is a lesser-known form of poetry than the more famous free verse poem style, but it is similar in its lack of rhyme. This is the distinguishing characteristic of blank verse poetry.
There are various types of poems that do not make use of rhyme, but the thing that sets blank verse apart is that even though it does not include rhyme, it does include a very specific meter structure.
Meter is a common feature in poetry that entails the way in which syllables are stressed, and this stressed form is typically arranged in a specific formation. One of the most common forms of meter formation is iambic pentameter, and this form is particularly common in blank verse poetry. This allows blank verse poetry to maintain a certain structure while eschewing rhyme. One of the most famous examples of blank verse poetry is the lengthy narrative poem Paradise Lost by John Milton.
 A Noted Bard. Writing a Poem in Blank Verse to lay before Sr. R- on the great Necessity at this time for an Act of Insolvency associated with Robert Walpole (c. 1737); British Museum, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
A Noted Bard. Writing a Poem in Blank Verse to lay before Sr. R- on the great Necessity at this time for an Act of Insolvency associated with Robert Walpole (c. 1737); British Museum, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Elegy Poetry
| Place of Origin | Ancient Greece |
| Era of Origin | 7th century BCE |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Traditionally ABAB |
| Famous Example | In Memory of W.B. Yeats by W.H. Auden |
The elegy is a type of poetry that is quite similar to an ode. The idea behind an elegy is that it is specifically focused on a specific person, although it could also be focused on a specific event or place (but the focus on a person is far more common). The distinguishing thematic element of the elegy is that it focuses on loss, and this is why most traditional elegies are about mourning.
 The Poems of Thomas Gray, Design 107, Elegy Written in a Country Church-Yard by William Blake (between 1797 and 1798); William Blake, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Poems of Thomas Gray, Design 107, Elegy Written in a Country Church-Yard by William Blake (between 1797 and 1798); William Blake, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The traditional elegy is written in a quatrain structure, and they often make use of iambic pentameter.
However, while a rhyme scheme like ABAB is somewhat commonly used in elegies, this is not necessarily always the case as the form can be changed and adapted to suit the specific needs of the poet. However, the focus on loss and mourning is a necessary component of the elegy, and some of the most famous examples of this type of poetry would be a poem like In Memory of W.B. Yeats by W.H. Auden. The mourning aspect, in this case, is prominently displayed in the name of the poem itself.
Epic Poetry
| Place of Origin | Ancient Sumer |
| Era of Origin | Around 3000 BCE |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | Iliad and Odyssey by Homer |
Epic poetry is one of the oldest types of poetry and it is also generally one of the longest. An epic poem is a narrative poem, but generally, the longest form of narrative poetry as it is focused on a detailed account of some kind of a narrative. In terms of the traditional usage of the term, this poem style typically focuses on heroes who go on some kind of a grand adventure. The name itself comes from the ancient Greek words epos meaning “word” or “song” via eipein meaning “to say”.
 Writing tablet inscribed with lines 468-473, Book I of Homer’s Iliad in Greek. From Egypt (400-500 CE); Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg), CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Writing tablet inscribed with lines 468-473, Book I of Homer’s Iliad in Greek. From Egypt (400-500 CE); Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg), CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
While ancient Greek epics were composed in hexametrical verse, epic poetry does not necessarily make use of any kind of specific rhyme scheme or meter structure. Some epic poems can also be hundreds of pages long, and as a result, they do not often make use of specific structures that one may associate with far shorter poems.
Two of the most famous examples of epic poetry are The Iliad and The Odyssey by the ancient Greek poet Homer. These particular poems have become some of the most important and influential in the entire Western literary canon.
Erasure Poetry
| Place of Origin | United States |
| Era of Origin | 1960s |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | Radi Os by Ronald Johnson |
Erasure or Blackout poetry is a relatively recent type of poetry, but it has become increasingly prominent, especially on social media. The idea behind erasure poetry is rather simple, and it involves taking an already existing text (which does not need to be a poem but easily can be) and erasing parts of it to create a new poem from what remains.
This could mean that one takes an article from a newspaper or a page from a book and black out all the words that are not desired to make something entirely new.
 Example of erasure poetry published in Army Time (2015); Michael Anthony, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Example of erasure poetry published in Army Time (2015); Michael Anthony, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
These poems, in recent years, can often be found on places like Twitter, where someone will back out words from tweets to create a new message. While those engaging in this may not think of it as poetry, it can be seen as a form of it. The earliest examples of this are the erasure poems of Doris Cross, but she is not particularly well known, and erasure poetry does not have any immensely big names, although there are cases like Radi Os by Ronald Johnson (which erases parts of Paradise Lost by John Milton to create something new).
Free Verse Poetry
| Place of Origin | France |
| Era of Origin | Late-19th century |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | Daddy by Sylvia Plath |
Free verse poetry tends to be associated with more contemporary types of poems, but this association is not necessarily entirely true, although it is a newer form. The basic idea behind free verse poetry is that there are no rules. A free verse poem does not need to have a particular structure, rhyme scheme, meter, or anything else that one may generally associate with poetry. It is a free form of poetry that allows the poet to create their own rules.
 The hours rise up by e. e. cummings painted onto a building in Leiden, The Netherlands; Tubantia, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The hours rise up by e. e. cummings painted onto a building in Leiden, The Netherlands; Tubantia, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
It is quite common for free verse poetry to mimic real-world language in some sense rather than sticking to a more stringent form of poetry that one may typically associate with more common forms of poetry like a sonnet. This means that some free verse poems, when read aloud, can sound like a piece of prose.
Some of the most famous examples of free verse poetry include experimental poetry like the work of e. e. cummings or more intimate forms like Daddy by Sylvia Plath.
Limerick Poetry
| Place of Origin | England |
| Era of Origin | Early-18th century |
| Number of Lines | Five |
| Rhyme Scheme | AABBA |
| Famous Example | Hickory Dickory Dock by an unknown writer |
The limerick is often considered to be one of the more entertaining types of poems. The basic premise behind the limerick is that it is a short, single-stanza poem with a rhyme scheme of AABBA. The short length of the limerick has led to them being used in more trivial or humorous settings.
It is especially common for the first four lines to serve as something of a setup while the final line delivers a comedic punchline.
 Plaque inscribed with a limerick poem at the corner of O’Donnell Street and Glentworth Street in Limerick, Ireland; Sheila1988, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Plaque inscribed with a limerick poem at the corner of O’Donnell Street and Glentworth Street in Limerick, Ireland; Sheila1988, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
While there may be examples of more serious limericks, they are certainly not the most famous of them all, and individual limericks are also generally not all that well known. However, limericks are prominently used for their fun rhyme scheme and structure for children-oriented nursery rhymes, such as Hickory Dickory Dock (although this particular example makes use of limericks throughout its stanzas).
Lyric Poetry
| Place of Origin | Ancient Greece |
| Era of Origin | Early-7th century BCE |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | The Heart Asks Pleasure First by Emily Dickinson |
The lyric poem is another of the oldest types of poems structured, most commonly, around feelings. The lyric poem is, quite often, a short poem that makes use of a musical quality. However, these poems are more focused on a rhythm than any kind of rhyme scheme or necessary structure. In addition, as they share a lineage with other ancient Greek forms like the epic, it is worth noting that the lyrical form does not focus on a narrative.
The focus on feelings over a narrative has contributed to the lyric poem having a strong influence on contemporary music, and as the musical term “lyrics” comes from this form of poetry, that influence does make some degree of sense.
One of the most famous examples of lyric poetry is The Heart Asks Pleasure First by Emily Dickinson.
 So Get Up lyric collage by Ithaka Darin Pappas (1992); IthakaDarinPappas, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
So Get Up lyric collage by Ithaka Darin Pappas (1992); IthakaDarinPappas, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Narrative Poetry
| Place of Origin | Ancient Sumer |
| Era of Origin | 2500 BCE |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | The Road Not Taken by Robert Frost |
Narrative poetry is a very broad label in terms of the many poem styles in the world. Narrative poetry is more of an all-encompassing term that allows other forms of poetry to fall under it. For instance, epic poetry is a form of narrative poetry. The narrative poem has its earliest origins in the prehistoric oral tradition, but the earliest instances of it being recorded put this form as one of the oldest types of poetry.
Narrative poetry, as the name suggests, is a form of poetry that focuses on telling a story of some kind. This means that it has variable length and structure.
 Writing tablet inscribed with lines 468-473, Book I of Homer’s Iliad in Greek. From Egypt (400-500 CE); Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg), CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Writing tablet inscribed with lines 468-473, Book I of Homer’s Iliad in Greek. From Egypt (400-500 CE); Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg), CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
There is no actual definitive rhyme scheme or meter for the narrative poem, and a narrative poem could, therefore, be any other type of poetry. For instance, one could tell a narrative within a sonnet, and that would lead that sonnet to also be an example of narrative poetry. The most ancient of all the known narrative poems are those like the Epic of Gilgamesh, which is thousands of years old and very long. However, one could also see something like Robert Frost’s The Road Not Taken as a far shorter example of narrative poetry.
Ode Poetry
| Place of Origin | Ancient Greece |
| Era of Origin | Around 500 BCE |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | Ode to a Nightingale by John Keats |
The ode is one of the oldest forms of poetry ever created, and they are also some of the most well-known forms of poetry. The basic idea behind an ode is that it is a poem in dedication to something.
An ode is quite similar to an elegy, but while an elegy focuses on a poetic object (often a person) through a sorrowful and generally mournful lens, the ode is a celebration, a tribute, or a song of praise.
 Ode to Pomegranate and Melon Vine poem by Wang Ao and painting by Shen Zhou (c. 1506-1509); Shen Zhou (painting) and Wang Ao (poem), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Ode to Pomegranate and Melon Vine poem by Wang Ao and painting by Shen Zhou (c. 1506-1509); Shen Zhou (painting) and Wang Ao (poem), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Odes do not need to make use of a particular form, rhyme scheme, or meter, but they are generally formal in tone. Additionally, they are particularly ancient and can be found throughout ancient Greek sources, and the traditional form of the ode was set to music. Some of the most famous include poems such as Ode to a Nightingale by John Keats. However, one could also point towards some instances of contemporary music as following the tradition of the ode to some extent.
Prose Poetry
| Place of Origin | Germany |
| Era of Origin | Early-19th century |
| Number of Lines | Any |
| Rhyme Scheme | Any |
| Famous Example | Spring Day by Amy Lowell |
Prose poetry is a relatively recent form of poetry as it only originated in the 19th century. This may appear old in general terms, but as a type of poetry like the epic is thousands of years old, the prose poem is practically a child in comparison.
The basic premise behind the prose poem is that it combines elements of both prose and poetry. This can mean that it makes use of standard prose structures and may look like a paragraph of text at first glance, but it will use poetic techniques, such as rhyme, meter, alliteration, and so on.
There are instances of actual prose that also make use of more poetic forms, such as some of the work of Herta Müller, like The Passport. However, that is a novel that uses poetic forms rather than a poem that uses prose forms. Something like Spring Day by Amy Lowell includes a few segments that are examples of prose poetry. The father of the Beat Movement, Jack Kerouac developed a style he called “spontaneous prose” that drew on the principles of prose poetry as spontaneous and devoid of edits.
 Memorial plaque to Jack Kerouac with an excerpt from his book On the Road in San Francisco’s Chinatown; Goodshoped35110s, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Memorial plaque to Jack Kerouac with an excerpt from his book On the Road in San Francisco’s Chinatown; Goodshoped35110s, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Sestina Poetry
| Place of Origin | France |
| Era of Origin | 12th century |
| Number of Lines | 39 |
| Rhyme Scheme | ABCDEF |
| Famous Example | Six Bad Poets by Christopher Reid |
Sestina poetry is an extremely precise form of poetry that makes use of an extremely complex form. It makes use of six stanzas, which are all made up of six lines, and this is then followed up with a concluding stanza of three lines. This brings the full poem length to 39 lines. However, the first stanza serves as a template for the rest, as the last word of each of those first six lines is then used as the last word of each line in every other stanza, but the order of the ending words follows a set pattern that rotates.
This is an extremely complex type of poetry, and the pattern in which the end words are used is known as Retrogradatio cruciate. There is a particular mathematical formula for the arrangement of the words.
 Diagram of the algorithm for ordering repeated words in a sestina; Phil wink, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Diagram of the algorithm for ordering repeated words in a sestina; Phil wink, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
A good example of this form is Six Bad Poets by Christopher Reid. A poem style like this is generally not recommended for those who are new to writing poetry.
Sonnet Poetry
| Place of Origin | Italy |
| Era of Origin | 13th century |
| Number of Lines | 14 |
| Rhyme Scheme | ABBA CDCD EFEF GG or ABBAABBA CDECDE |
| Famous Example | Shall I Compare Thee to a Summer’s Day by William Shakespeare |
The sonnet is probably the most famous poem in the English language even though it does not have its origins in England at all. The earliest sonnets were found in Italy, but the English form has since become immensely famous in the tradition of English poetry because it was the most common form that William Shakespeare made use of when he was writing his many poems.
The basic structure of the sonnet entails the use of fourteen lines arranged around a specific rhyme scheme. The most common of those rhyme schemes are the Shakespearean sonnet and the Petrarchan sonnet.
Sonnets are often based around love, but this is not always necessarily the case. There are also other sonnet rhyme schemes, but the two that have been mentioned are the most famous of them all.
 On the Sonnet by Dante Gabriel Rossetti (1880); Dante Gabriel Rossetti, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
On the Sonnet by Dante Gabriel Rossetti (1880); Dante Gabriel Rossetti, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Villanelle Poetry
| Place of Origin | France |
| Era of Origin | 16th century |
| Number of Lines | 19 |
| Rhyme Scheme | ABA and ABAA |
| Famous Example | Do Not Go Gentle Into That Good Night by Dylan Thomas |
Villanelles are another complex form of French poetry, and they are made up of a nineteen-line structure in which there are five tercets and an ending quatrain.
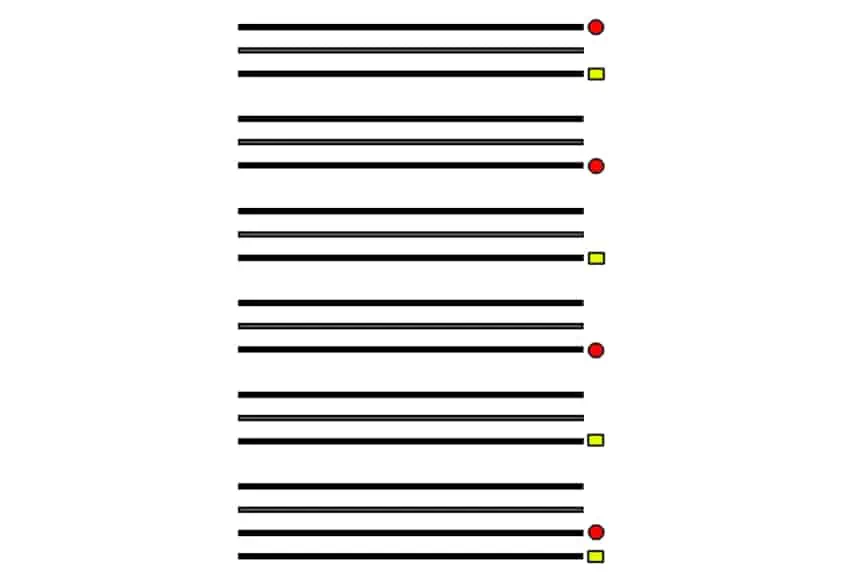 Visual representation of the structure and rhyme scheme of a villanelle; 3wnos, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Visual representation of the structure and rhyme scheme of a villanelle; 3wnos, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The tercets, which are three-line stanzas, make use of an ABA rhyme scheme while the final quatrain makes use of an ABAA rhyme scheme.
However, that is not everything. The true complexity of the form comes from its repetitive nature. The villanelle form entails lines 1, 6, 12, and 18 being repeated while lines 3, 9, 15, and 19 are also repeated. This means that the refrains need to be significant in some sense. Perhaps the most famous example of a villanelle is Do Not Go Gentle Into That Good Night by Dylan Thomas.
There are many different types of poems in this world that we all share with one another, and this article has examined only fifteen of those poem styles. There are many more that we did not examine, but we have looked at some of the most prominent types of poems with examples. Hopefully, you have learned about a few of the lesser-known types of poetry, but there are many other forms that were not included in this list. They too are worthy of our time and attention, so if you get a chance, see what else there is to read in this world of ours!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Poem?
A poem is a type of creative writing that, generally, makes use of a specific dedication to language. There are many different types of poems, and defining what a poem actually is can be a rather difficult thing. This is why we generally define many literary forms by what they are not. A poem is, therefore, not a piece of prose or dramatic writing. Some of the most common characteristics of poetry are rhythm, rhyme, and meter. However, a poem does not need to make use of any of these characteristics.
How Many Types of Poetry Exist?
This is an impossible question to answer because there are countless types of poems in our world. Many of them are still being created. For instance, while narrative poetry may be thousands of years old, erasure poetry is only a few decades old. New types of poetry are constantly being developed and iterated on, and some types of poems were even created by individual people and have since become their own poem styles that are replicated repeatedly. Perhaps a new type of poetry will be invented today. Who knows?
What Is the Most Famous Type of Poem?
Fame is based on location and subjectivity, but in the English-speaking world, it is quite likely that the sonnet is the most famous type of poem structure. The sonnet makes use of a fourteen-line structure and there are a few different types of sonnets that make use of different rhyme schemes. However, the reason for the fame of the sonnet in English is likely because it was the preferred poetic form that William Shakespeare adopted.
What Is the Oldest Type of Poem?
Narrative poetry is likely the oldest type of poem, and within the narrative poetry tradition, the epic poem is likely the oldest. These poems date back further than ancient Greece, although many of the most famous examples of epic poetry are ancient Greek. For instance, the works of Homer are some of the oldest examples of this particular type of poetry.
What Is the Longest Type of Poem?
Any poem that does not make use of a specific line count could, theoretically, be extended into a very long poem. However, the longest poems are generally narrative epic poetry. The longest of them all is the Mahābhārata. This ancient Indian poem has over 200,000 lines and 1.8 million words. This makes it significantly longer than the Christian Bible or all the works of Shakespeare combined. Therefore, it is a rather long poem!
In 2005, Charlene completed her wellness degrees in therapeutic aromatherapy and reflexology at the International School of Reflexology and Meridian Therapy. She worked for a company offering corporate wellness programs for several years before opening her own therapy practice. In 2015, she was asked by a digital marketer friend to join her company as a content creator, and it was here that she discovered her enthusiasm for writing. Since entering the world of content creation, she has gained a lot of experience over the years writing about various topics such as beauty, health, wellness, travel, crafting, and much more. Due to various circumstances, she had to give up her therapy practice and now works as a freelance writer. Since she is a very creative person and as a balance to writing likes to be active in various areas of art and crafts, the activity at acrylgiessen.com is perfect for her to contribute their knowledge and experience in various creative topics.
Learn more about Charlene Lewis and about us.