Unity and Variety in Art – How Artists Employ Visual Elements
This post may contain affiliate links. We may earn a small commission from purchases made through them, at no additional cost to you.
Artists use a wide range of techniques and elements to create captivating works of art that inspire and engage the viewer. Two critical technical qualities that artists often use to achieve this goal are unity and variety. Unity in art refers to the coherence and harmony of its elements, where all parts work together to create a unified whole. On the other hand, variety in art involves the use of diverse elements and techniques within the piece, creating a sense of interest, contrast, and complexity. In this article, we will explore unity art’s definition, variety art’s definition, examine examples of unity in art and examples of variety in art, and discuss how artists use these technical qualities to create captivating and engaging works of art.
Table of Contents
Unity Art’s Definition: What Is Unity in Art?
The technical quality of unity in an artwork refers to the coherence and harmony of its elements, where all parts work together to create a unified whole. Unity in art is achieved when all the elements and principles of design are balanced and integrated, creating a sense of completeness and harmony.
How Is Unity Created by Artists?
In a 2D composition, unity can be achieved through various means, such as the use of a consistent color scheme, repetition of shapes or motifs, and the careful arrangement of components in the composition. In painting, for example, an artist may create unity by using a limited palette, such as a monochromatic color scheme, or by repeating certain colors or shapes throughout the painting. In drawing and printmaking, unity can be achieved by controlling line quality, creating a consistent visual texture, and using a balanced composition.
In 3D compositions, such as sculptures and performance art, unity is achieved by carefully considering the relationship between the different elements of the piece. In sculpture, for example, an artist may create unity by using a consistent material, such as bronze or marble, or by repeating certain shapes or motifs throughout the piece. In performance art, unity can be created by carefully choreographing the movements of the performers and the placement of props and set pieces.
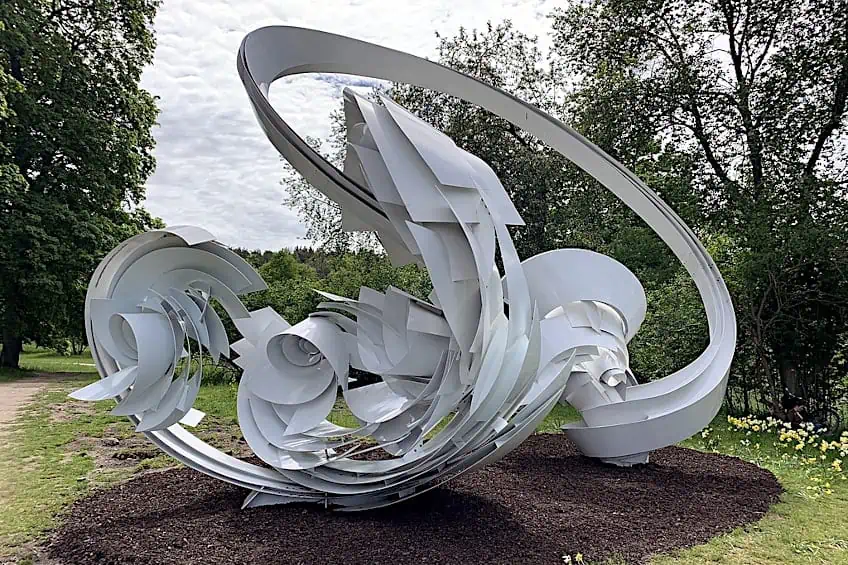 Hoop-La by Alice Aycock (2014); Oliviaefan, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Hoop-La by Alice Aycock (2014); Oliviaefan, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Different Kinds of Unity in Art
Art is a form of expression that allows individuals to communicate complex ideas and emotions in a visual and tactile way. One of the critical technical qualities that artists use to achieve this goal is unity. There are different kinds of unity in art, such as compositional unity, conceptual unity, and gestalt unity, each of which plays a crucial role in creating captivating and engaging works of art.
Compositional Unity
Compositional unity refers to how the different elements of a composition are arranged and organized to create a unified whole. In painting, drawing, and printmaking, compositional unity can be achieved through careful consideration of the placement of elements, the use of color, and the creation of a balanced composition.
An example of a unity artwork is Vincent van Gogh’s (1853 – 1890) Starry Night (1889). The composition is organized around the central spiral of the sky, which creates a sense of movement and unity, while the repetition of small marks and dots throughout the painting creates a sense of harmony and continuity.
 The Starry Night by Vincent van Gogh (1889); Vincent van Gogh, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Starry Night by Vincent van Gogh (1889); Vincent van Gogh, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Furthermore, artists often make use of what is called triangle composition to inspire a sense of unity in their artworks. The triangle composition is a technique in art that involves arranging the elements of a composition in a triangular shape. This technique is often used to create a sense of stability and balance in the composition, as the triangular shape is naturally harmonious and pleasing to the eye.
By using the triangle composition, artists can create a strong visual focal point and direct the viewer’s attention to the most critical elements of the artwork. Additionally, the use of a triangular shape can create a sense of unity in the artwork, as the viewer’s eye is naturally drawn to the center of the composition, creating a cohesive and harmonious whole.
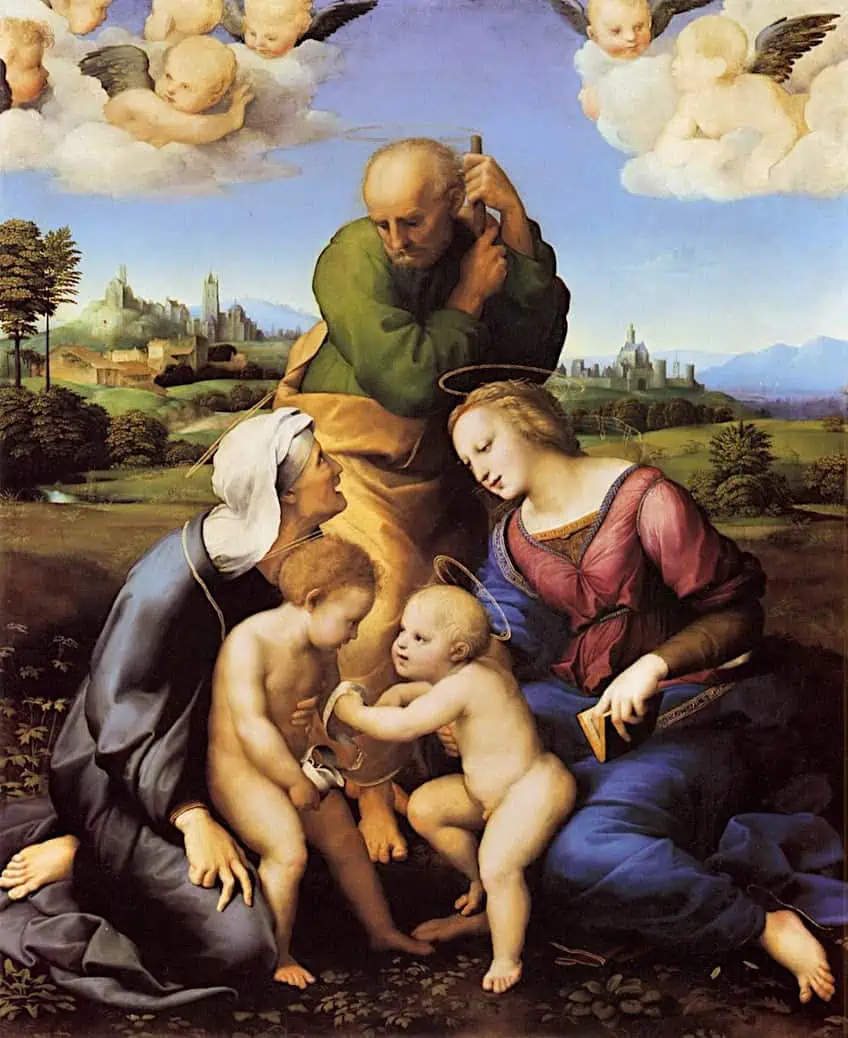 The Canigiani Madonna by Raphael (1507); Raphael, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Canigiani Madonna by Raphael (1507); Raphael, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Conceptual Unity
Conceptual unity, on the other hand, refers to the way in which an artwork’s meaning and ideas are communicated through its elements. In conceptual art, the ideas and concepts behind the work are often more critical than the actual physical elements.
Another unity artwork is Marcel Duchamp’s (1887 – 1968) Fountain (1917). A porcelain urinal is presented as a work of art, challenging traditional notions of art and authorship. The conceptual unity of the piece lies in its rejection of traditional aesthetic values and its embrace of conceptual art.
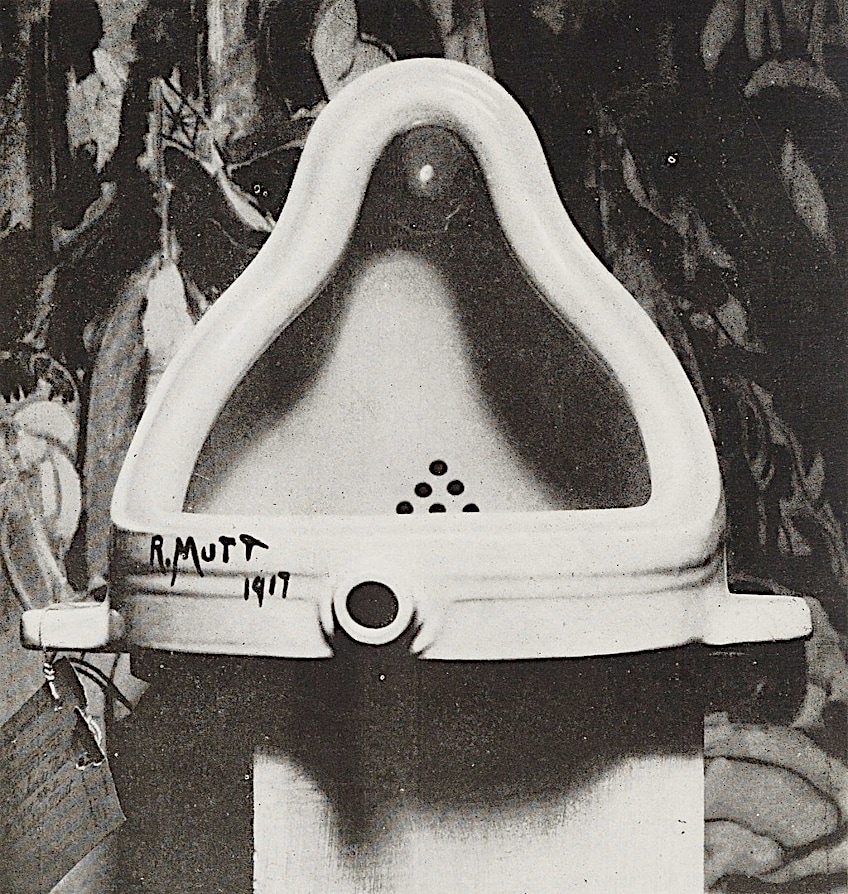 Fountain by Marcel Duchamp (1917); Marcel Duchamp, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Fountain by Marcel Duchamp (1917); Marcel Duchamp, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Gestalt Unity
Gestalt unity refers to the way in which our brains perceive the whole image as more than the sum of its parts. In other words, gestalt unity is how the human brain automatically organizes and makes sense of visual information.
For example, in Pablo Picasso’s (1881 – 1973) Les Demoiselles d’Avignon (1907), the figures are fragmented and distorted, but the viewer’s brain automatically perceives them as a unified whole. The gestalt unity of the piece lies in the way in which the fragmented figures are organized and arranged to create a cohesive composition.
What Is Variety in Art?
The technical quality of variety in an artwork refers to the use of diverse elements and techniques within the piece, creating a sense of interest, contrast, and complexity. Variety in art helps to break up the monotony of a composition and to create visual interest by showcasing different techniques, textures, and colors.
How Is Variety Created by Artists?
In a 2D composition, variety can be achieved by using different colors, textures, shapes, and sizes of elements. In painting, an artist may create variety by using contrasting colors, varying brush strokes, and layering different textures. In drawing and printmaking, variety can be created by experimenting with different line weights, textures, and patterns.
In 3D compositions, variety can be created by using a variety of materials, shapes, and techniques. In sculpture, an artist may use a combination of smooth and textured surfaces, or incorporate contrasting materials, such as wood and metal, to create visual interest. In performance art, variety can be created by incorporating different movements, sounds, and elements into the piece.
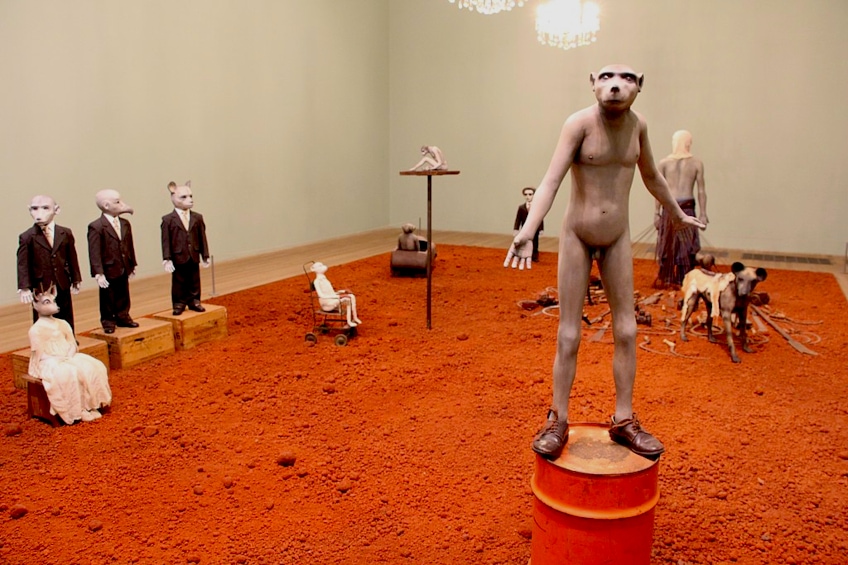 Installation view of Bankside African Adventure by Jane Alexander in the Tate Modern (1999-2002); Fred Romero from Paris, France, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Installation view of Bankside African Adventure by Jane Alexander in the Tate Modern (1999-2002); Fred Romero from Paris, France, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Different Kinds of Variety in Art
Variety is a technical quality in art that is used to create visual attraction, sophistication, and difference in an artwork. There are different kinds of variety in art, such as contrast, change and difference, and elaboration, each of which plays a crucial role in creating captivating and engaging works of art.
Contrast
Contrast refers to the use of different visual elements, such as color, texture, and shape, to create visual interest and tension in an artwork. In painting, drawing, and printmaking, contrast can be achieved through the use of complementary colors, high-contrast values, or the juxtaposition of different textures and shapes.
For example, in Edvard Munch’s (1863 – 1944) The Scream (1893), the high-contrast values and the use of complementary colors create a sense of tension and anxiety, emphasizing the emotional intensity of the scene.
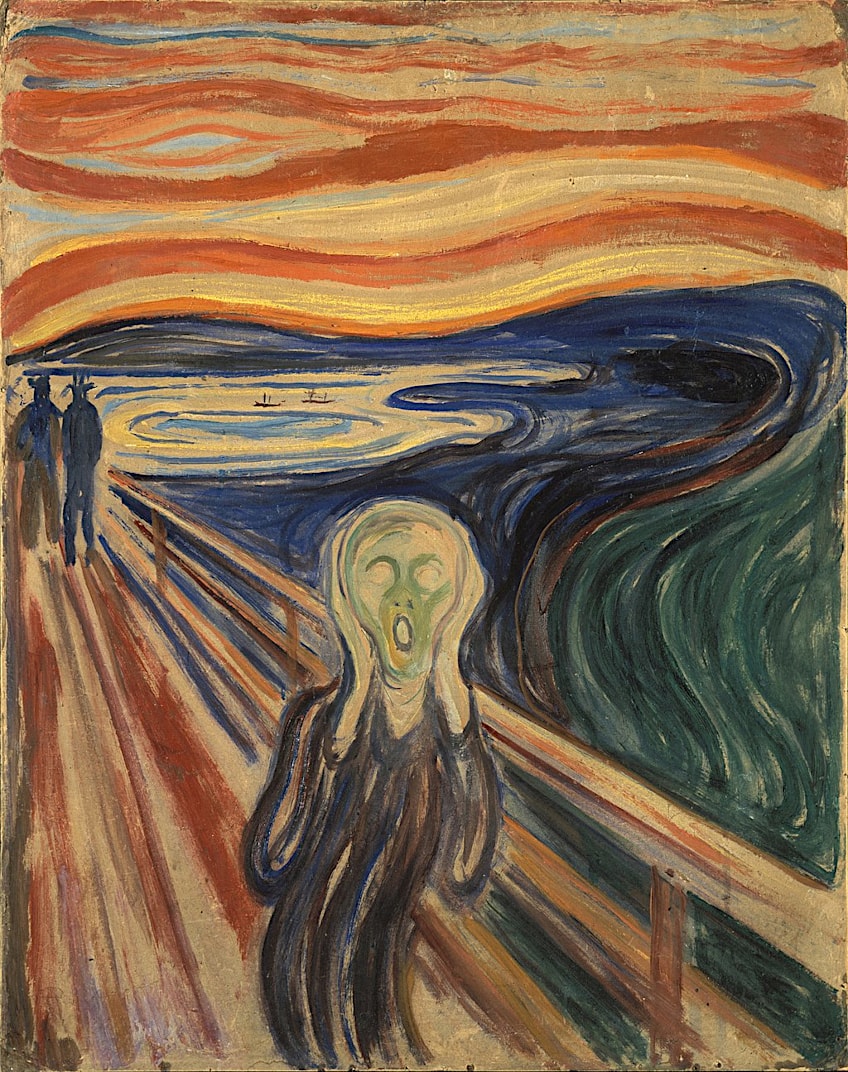 The Scream by Edvard Munch (1910); Edvard Munch, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Scream by Edvard Munch (1910); Edvard Munch, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Change and Difference
Change and difference refer to the use of variation and contrast to create a sense of movement and change in an artwork. In sculpture and performance art, change and difference can be achieved through the use of movement, sound, or light.
For example, in Alexander Calder’s (1898 – 1976) Mobile (1941), the movement and changing shapes of the suspended objects create a sense of playfulness and dynamism, engaging the viewer and drawing their attention to the artwork.
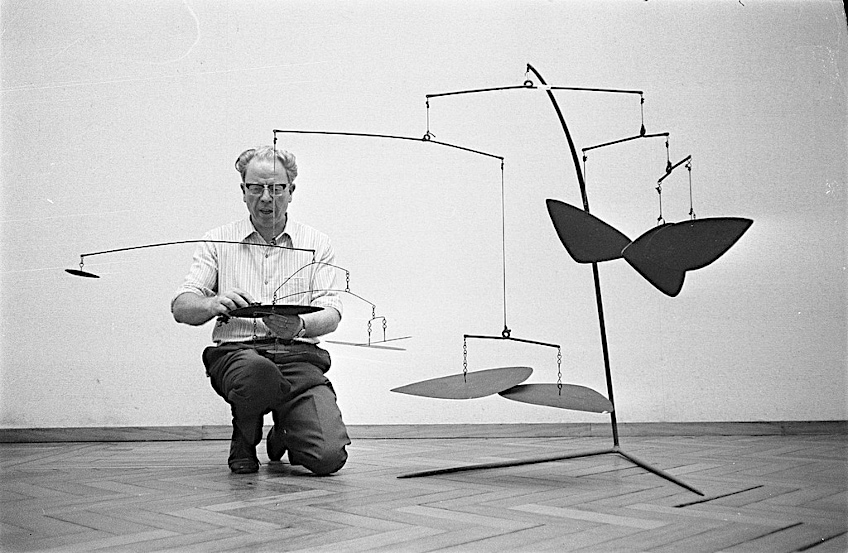 Photograph of Alexander Calder installing a Mobile taken in 1969; Eric Koch for Anefo, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Photograph of Alexander Calder installing a Mobile taken in 1969; Eric Koch for Anefo, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Elaboration
Elaboration refers to the use of repetition and variation to create a sense of complexity and interest in an artwork. In drawing, printmaking, and painting, elaboration can be achieved through the use of patterns, ornamentation, or the repetition of similar shapes or motifs.
For example, in Gustav Klimt’s (1862 – 1918) The Kiss (1907 – 1908), the elaborate patterns and the repetition of the circular shapes create a sense of opulence and decadence, emphasizing the sensual and romantic nature of the scene.
 The Kiss by Gustav Klimt (1907-8); Gustav Klimt, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Kiss by Gustav Klimt (1907-8); Gustav Klimt, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Artists Using Unity and Variety in Art Together
Artists frequently employ the technical qualities of unity and variety in art together in order to create visually compelling and engaging artworks. By skillfully balancing these elements in their compositions, artists can produce works that are both visually cohesive and intricate, attracting the viewer’s gaze and holding their attention. In this section of the article, we will look at more examples of unity in art and examples of variety in art.
Composition VIII (1923) by Wassily Kandinsky
| Artist | Wassily Kandinsky (1866 – 1944) |
| Date | 1923 |
| Medium | Oil on canvas |
| Dimensions (cm) | 140 x 201 |
| Style | Abstract Art |
| Location | Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, New York City, United States |
In this abstract painting, Kandinsky employs a complex and intricate composition that balances unity and variety in striking ways. The use of contrasting colors and shapes creates a sense of variety in the piece, drawing the viewer’s eye and adding visual interest. However, despite the variety of forms and colors used in the painting, the strong compositional unity created by the underlying geometric structure creates a sense of stability and balance, holding the viewer’s attention and conveying a powerful sense of order and harmony.
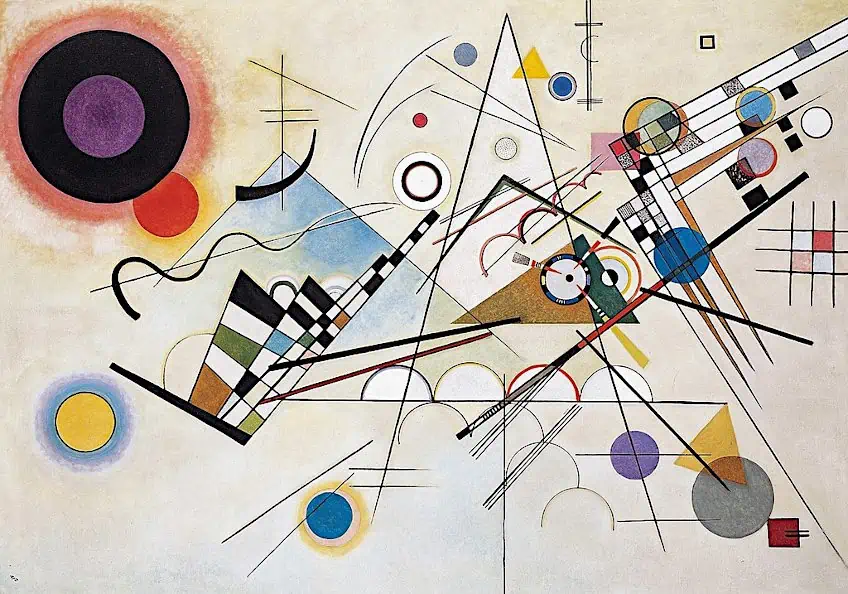 Composition VIII by Wassily Kandinsky (1923); Wassily Kandinsky, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Composition VIII by Wassily Kandinsky (1923); Wassily Kandinsky, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Infinity Mirrors series (1965 – Present) by Yayoi Kusama
| Artist | Yayoi Kusama (1929 – Present) |
| Date | Series running from 1965 to the present |
| Medium | Wood, metal, glass mirrors, plastic, acrylic panel, rubber, LED lighting system, acrylic balls, and water |
| Dimensions (cm) | N/A |
| Style | Installation |
| Location | Installations put on internationally |
In this immersive installation, Kusama uses mirrored rooms and a vast array of colorful, polka-dotted objects to create a unified yet varied experience for the viewer. The use of repetition and variation creates a sense of elaboration and complexity in the artwork, drawing the viewer’s eye and adding visual interest. Despite the variety of shapes and textures used in the installation, the strong compositional unity created by the repeating motifs and the overall mirrored environment creates a sense of harmony and balance, holding the viewer’s attention and creating a powerful emotional impact.
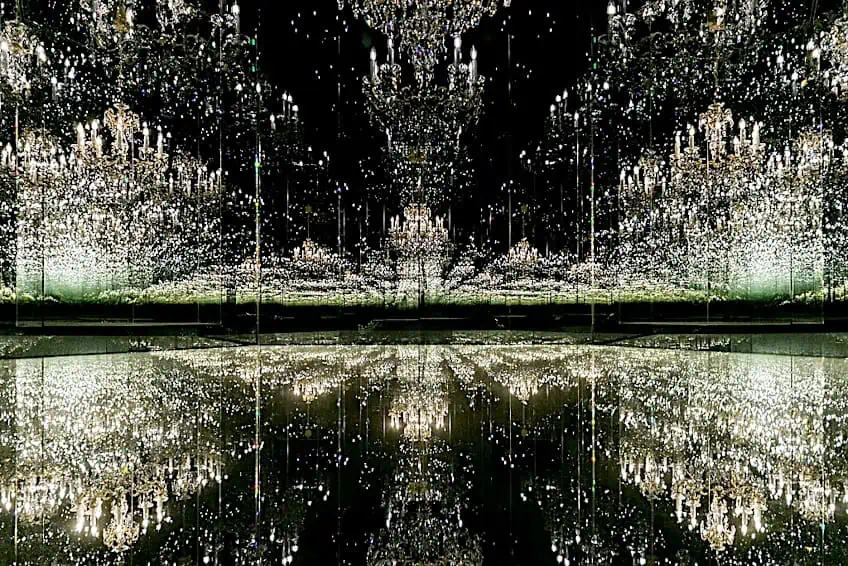 Chandelier of Grief from the Infinity Mirror Rooms series by Yoyai Kusama (2016/2018); Swarovski Kristallwelten, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Chandelier of Grief from the Infinity Mirror Rooms series by Yoyai Kusama (2016/2018); Swarovski Kristallwelten, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Sunflower Seeds (2008) by Ai Weiwei
| Artist | Ai Weiwei (1957 – Present) |
| Date | 2008 |
| Medium | Porcelain |
| Dimensions (cm) | N/A |
| Style | Installation |
| Location | Tate Modern, London, United Kingdom |
In this large-scale installation, Weiwei uses thousands of handcrafted ceramic sunflower seeds to create a unified whole that is also highly varied. The use of repetition and variation creates a sense of expansion and intricacy in the artwork, drawing the viewer’s eye and adding visual interest. However, despite the variety of shapes and textures used in the installation, the strong compositional unity created by the arrangement of the seeds into a vast, undulating sea creates a sense of harmony and balance, holding the viewer’s attention and creating a powerful emotional impact.
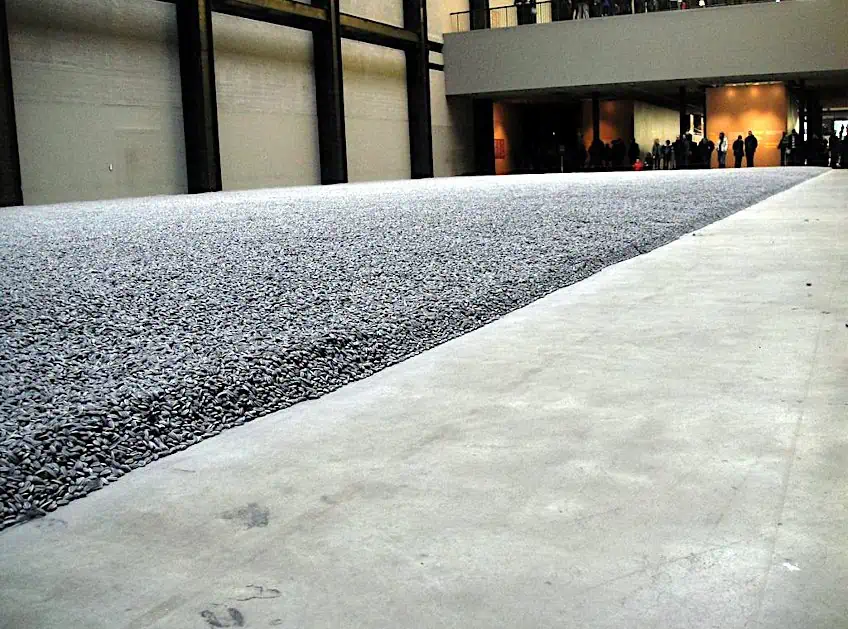

Installation view of Sunflower Seeds in the Tate Modern Turbine Hall (2008); Анна Астахова, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Seven Principles of Art Overview
- Principles of Art Overview
- Balance in Art
- Movement in Art
- Contrast in Art
- Pattern in Art
- Emphasis in Art
- Proportion and Scale in Art
In conclusion, unity and variety are essential technical qualities that artists use to create captivating works of art. Unity in art involves creating a sense of coherence and harmony, where all elements work together to create a unified whole. In contrast, variety in art involves using diverse techniques and elements to create visual interest, contrast, and complexity. Through careful use of these technical qualities, artists are able to create works that engage the viewer, highlight different techniques, and showcase their unique artistic vision. Through examining instances of both unity and variety in art, we develop a more profound admiration for the expertise, ingenuity, and practical prowess demanded to produce genuinely mesmerizing pieces of artwork.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Unity in Art?
Overall, unity art’s definition is the essential quality of art that helps create a sense of coherence and harmony in the work, allowing the viewer to connect with and appreciate the piece as a whole. This can be done in various technical ways, like using a consistent color scheme, repeating shapes or motifs, creating a sense of rhythm by repeating the same sound or movements in a Performance art piece, and more.
What Is Variety in Art?
Overall, variety in art is an important technical quality that helps to create interest and complexity within a piece. It can be used to highlight different techniques, textures, and colors, and to break up the monotony of a composition. By creating variety, artists can engage the viewer and create a sense of visual interest and complexity within the artwork.
Why Is Unity in Art Important?
Unity in art is a critical technical quality that allows artists to create captivating and engaging works of art. Whether achieved through compositional unity, conceptual unity, or gestalt unity, unity in art plays a crucial role in creating works that communicate complex ideas and emotions, challenge traditional notions of art, and engage the viewer on both an intellectual and emotional level. By exploring the different kinds of unity in art, we gain a deeper appreciation for the skill, creativity, and technical proficiency required to create truly remarkable works of art.
Why Is Variety in Art Important?
Variety in art is a critical technical quality that allows artists to create works that are visually compelling, emotionally engaging, and technically proficient. Whether achieved through contrast, change and difference, or elaboration, the incorporation of variety in art is essential to convey intricate concepts and sentiments, subvert conventional artistic conventions, and captivate the spectator’s mind and heart. By delving into the various forms of diversity in art, we acquire a more profound admiration for the techniques, creativity, and visual skills needed to produce unique pieces of artwork.
In 2005, Charlene completed her wellness degrees in therapeutic aromatherapy and reflexology at the International School of Reflexology and Meridian Therapy. She worked for a company offering corporate wellness programs for several years before opening her own therapy practice. In 2015, she was asked by a digital marketer friend to join her company as a content creator, and it was here that she discovered her enthusiasm for writing. Since entering the world of content creation, she has gained a lot of experience over the years writing about various topics such as beauty, health, wellness, travel, crafting, and much more. Due to various circumstances, she had to give up her therapy practice and now works as a freelance writer. Since she is a very creative person and as a balance to writing likes to be active in various areas of art and crafts, the activity at acrylgiessen.com is perfect for her to contribute their knowledge and experience in various creative topics.
Learn more about Charlene Lewis and about us.







